The superheterodyne radio was one of the most successful forms of radio being used almost exclusively as the RF circuit design topology of choice until recent years.
- It works on the principle of heterodyning which simply means mixing.
- The superheterodyne radio receiver mixes the received signal frequency with the frequency of the signal generated by a local oscillator.
Working of Superheterodyne Receiver
- The incoming signal of the superheterodyne receiver goes through the antenna and is filtered to reject the image frequency and then amplified by the RF amplifier.
- RF amplifier amplifies a particular carrier frequency within the AM broadcast range.
- The selected frequency and two sidebands are allowed to go through the amplifier.
- The carrier of the received signal is called radio frequency carrier and its frequency is radio frequency ƒRF and the local oscillator signal operates at ƒOSC.
- Then this amplified RF frequency is mixed with the local oscillator frequency.
- The mixer combines these two signals which produce the sum and difference of frequency signals of the incoming carrier signal and local oscillator signal, which are ƒOSC+ƒRF and ƒOSC-ƒRF.
- The (fOSC+fRF) sum of frequency is rejected by the filter and the remaining difference frequency (ƒOSC-ƒRF ) signal which is a down-converted frequency signal is called an intermediate frequency (IF) carrier (ƒIF= ƒOSC-ƒRF ).
- The original carrier signal and the IF carrier signal of the modulation is the same and it has a fixed frequency of 455kHz which is amplified by one or more stages of amplification.
- The IF amplifier amplified the IF signal which raises its level for the information extraction process.
- The IF amplifier fulfills the gain and bandwidth requirements of the receiver.
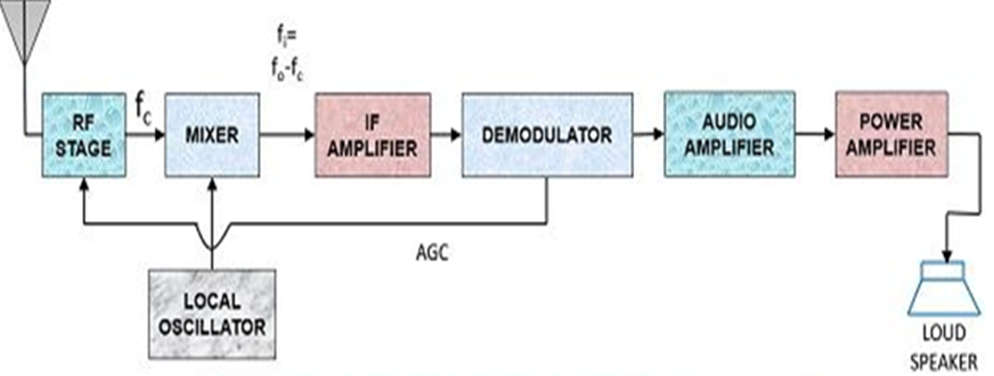
- The detector received the amplified IF signal to detect the information signal component from 455 kHz IF, to reproduce the original information data, which is generally in the form of the audio signal.
- The detector stage is used to eliminate one of the sidebands which are still present and separates the RF from the audio components of the other sideband.
- The RF component is filtered out and audio is applied to the audio stages for amplification.
- The amplified audio signal is then applied to the AF amplifier to increase the audio frequency level of the signal and to provide enough gain to drive the speaker or headphones.
- A speaker is connected to the AF amplifier to play the audio information signal.
- The superheterodyne receiver is Automatic gain control (AGC) which is given to the RF, IF and mixer stages to generate constant output irrespective of the varying input signal.
Advantages of Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
- It operates at a low signal level.
- The mixer provides fixed frequency operations.
- Provides excellent selectivity and sensitivity.
- Good sensitivity: The super heterodyne format allowed for good levels of sensitivity to be reached when compared to various other types of radio receiver. Although other formats now offer comparable levels of sensitivity, the superhet was well ahead of others like the TRF, etc. in the early days of wireless communications.
Disadvantages of Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
- Overall system cost is increased as additional circuits are used.
- The issue of picture frequency is one of the superheterodyne receiver’s main drawbacks.
- An image frequency is an unwanted input frequency that is equal to the station frequency plus (or minus) twice the intermediate frequency in heterodyne receivers.
Applications of Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
- It is used in various places like Television, Radio receivers, commercial radios.
- A radio receiver known as a superheterodyne, or superhet for short, employs frequency mixing to change a received signal’s carrier frequency into a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) that can be processed more easily.
