A transformer is a magnetic component or an electric component which transforms electrical a.c. power from one circuit to another circuit without changing the frequency. It works on principle of mutual inductance.
Transformers are capable to of either increasing or decreasing the voltage and current levels of their supply, without modifying its frequency, or the amount of electrical power being transferred from one winding to another via the magnetic circuit.
Construction:
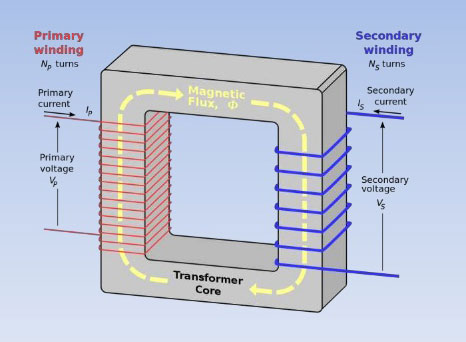
It consists of two highly inductive coils which are electrically separated, but magnetically linked through an iron core of low reluctance. The two coils possess high mutual inductance.
- It one coil L1 primary coil, is connected to an a.c. source, an alternating flux is set up in the laminated core, most of which is linked with the other coil.
- Hence, mutually induced voltage is produced in the second coil.
- If the second coil L2 is closed, the current through it and so electrical energy is transferred from the primary coil L1 to the secondary coil L2.
- It should be noted that a steady current cannot produces induced voltages.
Types of transformers:
The various types of transformers are as given below.
- Modular transformers.
- AF transformers.
- RF and AF transformers.
- Broadband transformer.
- Power transformers.
- Voltage transformers.
- Current transformers.
- Impedances transformers.
- Isolation transformers.
- Line transformers.
- Auto transformer.
- Pulse transformers.
- Peaking transformers.
- Interstage transformers.
