- A pH sensor is a device used to determine the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, also known as pH. The unit of measurement for acidity or alkalinity is pH. It is graded on a scale of 0 to 14.
- The pH value provides quantitative information that expresses the degree of activity of an acid or base in terms of hydrogen ion activity. The pH of a substance is proportional to the concentrations of hydrogen ion [H+] and hydroxyl ion [OH-]. If the H+ concentration exceeds the OH- concentration, the material is acidic, with a pH of less than 7. If the OH- concentration is greater than the H+ concentration, the material is basic, with a pH greater than 7.
- When equal amounts of H+ and OH- ions are present, the material has a pH of 7. Free hydrogen and hydroxyl ions are present in acids and bases, respectively.
- For a given set of conditions, the relationship between hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions in a given solution is constant, and either one can be determined by knowing the other.

Working of pH Sensor
- A pH sensor/meter is used in pharmaceuticals to determine the pH of various solutions. It is a more accurate method than the pH probe, which sends electrical signals to the pH meter, which displays the solution’s pH value.
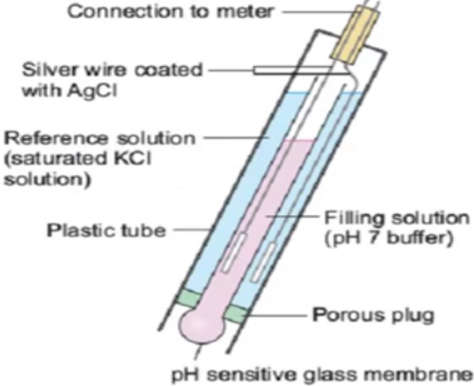
- A sensor electrode and a reference electrode are located on the glass pH probe. These electrodes are made of glass tubes, one of which contains a pH 7 buffer and the other a saturated potassium chloride solution. The sensor electrode bulb is made of porous glass or a permeable glass membrane that has been coated with silica and metal salts.
- In the bulb, a silver wire coated with silver chloride is immersed in the pH7 buffer. As shown in the figure below, another silver wire coated with silver chloride is immersed in the saturated potassium chloride solution in the reference electrode.
- When the pH probe is immersed in a solution, hydrogen ions accumulate around the bulb and replace the metal ions in the bulb. This ion exchange produces some electric flow, which is captured by the silver wire.
- The voltage of this electric flow is measured by the pH meter by converting it into pH value by comparing the generated voltage with the reference electrode.
- As the acidity of the solution increases, so does the concentration of hydrogen ions, which raises the voltage. The increased voltage lowers the pH reading on the pH meter.
- Similarly, an increase in alkalinity decreases the concentration of hydrogen ions or increases the concentration of hydroxyl ions, which decreases the voltage and increases the pH value in a pH meter.
- The overall operation of the pH sensor and pH meter is based on the exchange of ions from the sample solution to the inner solution (pH 7 buffer) of the glass electrode via the glass membrane. The porosity of the glass membrane decreases with continued use, lowering the probe’s performance.
Advantages of pH Sensor
- It is used in a wide range of applications, including cheese making, pool maintenance, growing healthier plants by measuring soil pH, stain removal, and so on.
- The meters directly provide a numerical value for the pH.
- With the help of pH sensors, pH meters are extremely accurate and provide precise pH values.
- It is useful in determining how acidic or basic a substance is.
Disadvantages of pH Sensor
- They are prohibitively expensive.
- Calibration of pH meters is required.
Applications of pH Sensor
- The following industries make extensive use of pH meters.
- Food & beverage.
- Pharmaceutical.
- Oil & gas.
- Water treatment plant.
- In the agricultural industry, pH measurement is critical for soil evaluation. Because major crops require an alkaline environment, pH measurement is required.
- It becomes an important factor in detergent production.
- Monitoring pH levels is critical in water treatment plants and RO water purifiers.
