- An infrared (IR) sensor is an electronic device that measures and detects infrared radiation in its surrounding environment.
- William Herschel, an astronomer 1800 accidentally discovered Infrared Radiation, as he was measuring the temperature of each color of the light ( separated by a prism ), he noticed that the temperature just beyond the red light was highest.
- IR is invisible to the human eye, as its wavelength is longer than that of visible light ( though it is the same on the electromagnetic spectrum ). Anything gives off infrared radiation ( everything that has a temperature above around five degrees Kelvin).
Types of IR Sensor
Active IR Sensor
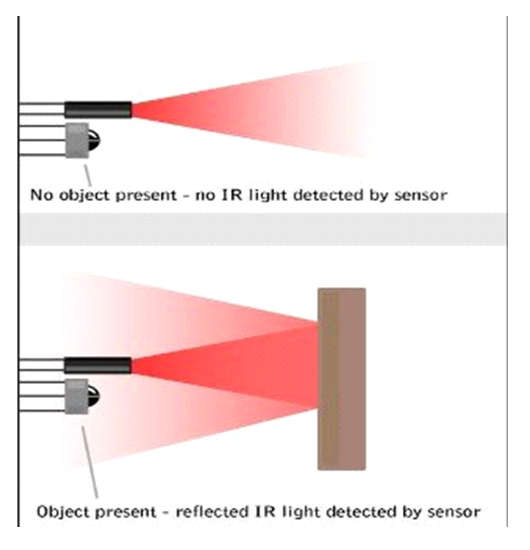
Active infrared sensors both emit and detect infrared radiation. Active IR sensors have two parts: a light-emitting diode (LED) and a receiver. When an object comes close to the sensor, the infrared light from the LED reflects off of the object and is detected by the receiver. Active IR sensors act as proximity sensors, and they are commonly used in obstacle detection systems (such as in robots).
Passive infrared (PIR) sensors only detect infrared radiation and do not emit it from an LED. Passive infrared sensors are comprised of
- Two strips of pyroelectric material (a pyroelectric sensor)
- An infrared filter (that blocks out all other wavelengths of light)
- A fresnel lens (which collects light from many angles into a single point)
- A housing unit (to protect the sensor from other environmental variables, such as humidity)
Passive Infrared Sensor
- PIR sensors are most commonly used in motion-based detection, such as in-home security systems. When a moving object that generates infrared radiation enters the sensing range of the detector, the difference in IR levels between the two pyroelectric elements is measured. The sensor then sends an electronic signal to an embedded computer, which in turn triggers an alarm.
- The best examples of PIR sensors are bolometers, Pyro-Electric Detector, Thermocouple-Thermopile, etc. PIR sensors are available in two types thermal IR sensors and quantum IR sensors.
Thermal Infrared Sensor
- These types of sensors are independent of wavelength and they utilize heat-like energy sources. These are slow along with the response time as well as detection time.
Quantum Infrared Sensor
- These types of sensors depend on wavelengths and the response time and detection time they have are high. These kinds of infrared sensors need repeated cooling for exact measurement.
IR Sensor Module
The IR sensor module includes five essential parts IR Tx, Rx, Operational amplifier, trimmer pot (variable resistor) & output LED. The pin configuration of the IR sensor module is discussed below.
- VCC Pin is power supply input
- GND Pin is the power supply ground
- OUT is an active-high o/p
The main specifications and features of the IR sensor module include the following.
- The operating voltage is 5VDC
- I/O pins – 3.3V & 5V
- Mounting hole
- The range is up to 20 centimeters
- The supply current is 20mA
- The range of sensing is adjustable
- Fixed ambient light sensor
How Infrared Sensor Works
- IR source (transmitter) is used to emit radiation of the required wavelength.
- This radiation reaches the object and is reflected.
- The reflected radiation is detected by the IR receiver.
- The IR Receiver detected radiation is then further processed based on its intensity. Generally, IR Receiver output is small and amplifiers are used to amplify the detected signal.
- Incidence in an IR Detection System may be direct or indirect. In the case of Direct Incidence, there is no hindrance between transmitter and receiver. Whereas, in Indirect Incidence, IR Transmitter and Receiver are kept side by side and the object is in front of them.
IR Sensor Circuit
- The application circuit of the IR sensor is an obstacle-detecting circuit that is shown below. This circuit can be built with a photodiode, IR LED, an Op-Amp, LED & a potentiometer, The main function of an infrared LED is to emit IR light and the photodiode is used to sense the IR light. In this circuit, an operational amplifier is used as a voltage comparator and the output of the sensor can be adjusted by the potentiometer based on the requirement.
- When the light emitted by the IR LED is incident on the photodiode after hitting an object, the resistance of the photodiode falls from a huge value.
- One of the inputs of the op–amp is at the threshold value set by the potentiometer. The other input to the op-amp is from the photodiode’s series resistor. When the incident radiation is more on the photodiode, the voltage drop across the series resistor will be high.
- In the IC, both the threshold voltage and the voltage across the series resistor are compared. If the voltage across the resistor series to photodiode is greater than that of the threshold voltage, the output of the IC Op – Amp is high.
- As the output of the IC is connected to an LED, it lightens up. The threshold voltage can be adjusted by adjusting the potentiometer depending on the environmental conditions.
- The positioning of the IR LED and the IR Receiver is an important factor. When the IR LED is held directly in front of the IR receiver, this setup is called Direct Incidence. In this case, almost the entire radiation from the IR LED will fall on the IR receiver. Hence there is a line of sight communication between the infrared transmitter and the receiver. If an object falls in this line, it obstructs the radiation from reaching the receiver either by reflecting the radiation or absorbing the radiation.
Advantages of IR Sensor
- Low power consumption.
- Noise immunity is strong.
- These sensors are not affected by rust.
- They do not need to get in touch with objects for detection.
- No data leakage because of the directionality of infrared radiation of ray.
- These are more modest in size and are more moderate.
- It responds very quickly as compared to thermocouples.
- It provides high reliability.
Disadvantages of IR Sensor
- Line of sight is necessary.
- It can be affected based on the conditions of the environment like fog, rain, pollution, dust, etc.
- These sensors can be blocked by common objects.
- The data rate transmission is not fast.
- Range is limited.
- High force IR signals can harm human eyes.
Applications of IR Sensor
- Rail Safety
- IR Imaging Devices
- Infrared Astronomy
- Optical Power Meters
- Night Vision Devices
- Sorting Devices
- Moisture Analyzers
- Missile Guidance
- Flame Monitors
- Remote Sensing
- Climatology
- Gas Analyzers
- Meteorology
- Rail safety
- Exploration of Petroleum
- Flame Monitors
- Testing of Anesthesiology
- Gas detectors
- Moisture Analyzers
- Water analysis