- The BME680 is a digital environmental sensor that measures pressure, humidity, and temperature. It’s the first gas sensor to combine high-linearity, high-accuracy gas, pressure, humidity, and temperature sensors.
- It is designed specifically for mobile applications and wearables where size and power consumption are critical. Depending on the operating mode, the BME680 ensures optimized consumption, long-term stability, and high EMC robustness. The BME680’s gas sensor can detect a wide range of gases, including volatile organic compounds, to measure air quality for personal well-being (VOC).
- To monitor indoor air quality, the BME680’s gas sensor can detect a wide range of volatile organic compounds. This sensor, like most gas sensors, is sensitive to multiple gases and alcohols but cannot distinguish between them. It will provide you with a single resistance value as well as the overall VOC content. As a result, it is best suited for measuring changes in a known gas density rather than detecting which is changing.
How Does the BME680 Gas Sensor Work?
- The MEMS technology is used to create the BME680 gas sensor, as opposed to the MQ2 and MQ3. Significant size, power, and functionality reductions, as well as an improvement in functionality and selectivity, are all benefits of MEMS-based gas detection.
- A typical MEMS gas sensor consists of a metal oxide semiconductor layer that serves as the sensing material and reacts with the target gas, at least two electrodes that track changes in electrical resistance/current, and a micro-hotplate that raises the working temperature.
- When the surface of a metal oxide semiconductor layer is heated to a high temperature, oxygen is adsorbed. Electrons from the metal-oxide conduction band are attracted to oxygen molecules in clean air. This creates a potential barrier by forming an electron depletion layer just beneath the surface of metal-oxide particles. As a result, the metal-oxide layer becomes highly resistive, preventing the flow of electric current.
- However, when gases are present, the surface density of adsorbed oxygen decreases as it reacts with the gases, lowering the potential barrier. After that, electrons are released into the metal-oxide layer, allowing current to freely flow through the sensor.
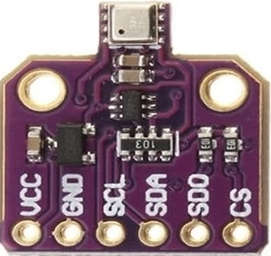
Pin Configuration of BME680 Environmental Sensor
The pin description of the BME680 Environmental sensor is given below.
- VCC: The power supply pin requires 1.7V to 3.6V for operation.
- GND: GND Pin.
- SCL: Serial Clock Pin for I2C Interface/ SCK Pin for SPI Communication.
- SDA: Serial Data Pin for I2C Interface/ MOSI Pin for SPI Communication.
- SDO: MISO Pin for SPI Communication.
- CS: Chip Select Pin for SPI Interface.
Features & Specifications of BME680 Environmental Sensor
- Voltage range: 1.7V to 3.6V.
- Temperature range of operation: -40°C to +85°C.
- Operating Humidity Range: 0 to 100% R.H.
- Operating Pressure: 300-1100hPa.
- The IAQ range is 0-500 PPM.
- I2C (up to 3.4MHZ)/ SPI interface (3 and 4 wire, up to 10MHz).
- I2C address: 0x76/0x77 (default) (optional).
- Standby current ranges from 0.29 to 0.8 uA.
- Sleep current ranges from 0.15 to 1 uA.
- Detection and measurement of VOCs (Ethane, Isoprene, Ethanol, Acetone, Carbon Monoxide).
Applications of BME680 Environmental Sensor
- Indoor air quality.
- Home automation and control.
- Internet of things.
- Weather forecast.
- Used in handheld devices like mobile phones, tablet PCs, GPS devices, Wearables, Watches.
- GPS enhancement (e.g. time-to-first-fix improvement, dead reckoning, slope detection).
- Indoor navigation (change of floor detection, elevator detection).
- Outdoor navigation, leisure, and sports applications.
- Vertical velocity indication (rise/sink speed).