- For a radio signal to carry information, it must be varied or modulated – there are various types of modulation, each best in different situations.
What is Modulation?
- Modulation is the technique that involved the two signals for the modulation process.
- The message is also called a baseband signal and this baseband signal is representing the original signal which is the band of frequencies.
- This original signal is to be transmitted to the receiver and the frequency of the signal is usually low.
- The other signal interacts with a high-frequency sinusoidal wave, this signal is known as the carrier signal.
- The carrier signal frequency is always higher than that of the original signal.
- The baseband signal amplitude is transferred to the high-frequency carrier.
- Therefore, modulation can be defined as, the process of superimposing a low-frequency signal on a high-frequency carrier signal.
Modulation Types
There are three types of modulation.
- Amplitude Modulation
- Frequency Modulation
- Phase Modulation
1. Amplitude Modulation:
- Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique that is used in electronic communication for transmitting messages with a radio wave.
- In AM, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal.
- The AM modulation index is a measure based on the ratio of the modulation excursions of the RF signal to the level of the unmodulated carrier.
- The amplitude modulation is the peak change in the RF amplitude from its unmodulated value. The modulation index is normally expressed as a percentage and may be displayed on a meter connected to an AM transmitter.
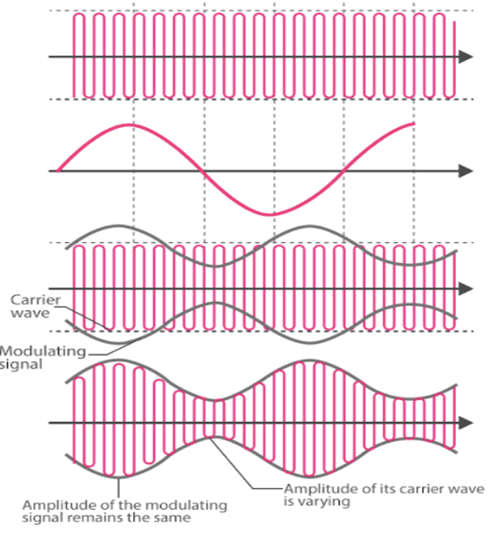
Applications of Amplitude Modulation
- Broadcast Transmissions: AM is used in broadcasting transmission over the short, medium, and long wavebands. Since AM is easy to demodulate radio receivers for amplitude modulation are therefore easier and cheaper to manufacture.
- Air-band radio: AM is used in the VHF transmissions for many airborne applications such as ground-to-air radio communications or two-way radio links for ground staff personnel.
- Single sideband: Amplitude modulation in this form is used for HF radio links or point-to-point HF links. AM uses a lower bandwidth and provides more effective use of the transmitted power.
- Quadrature amplitude modulation: AM is used extensively in transmitting data in several ways including short-range wireless links such as Wi-Fi to cellular telecommunications and others.
2. Frequency Modulation:
- The category of angle modulation in which the frequency of the carrier wave is changed according to the amplitude of the message signal is known as frequency modulation.
- The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing.
- It is widely used in analog modulation techniques.
- In frequency modulation both amplitude and phase of the carrier wave are unchanged and the only frequency can change the wave.
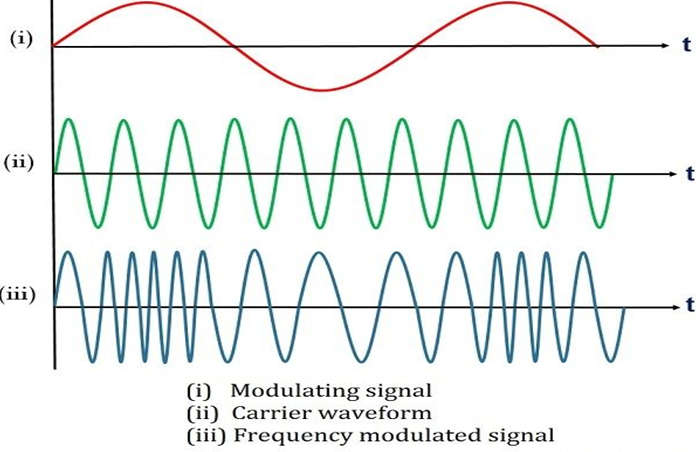
- The above figure shows the modulating signal that has to be transmitted.
- The second wave is the carrier wave and the frequency is varied according to the amplitude of the modulating signal.
- The last one is the frequency modulated signal that is transmitted after modulation is done.
Applications of Frequency Modulation
- It is used in radio signal broadcasting.
- During satellite and microwave communication, frequency modulation is widely used.
- It has extensive applications in cellular radio communication and TV sound transmission.
3. Phase Modulation:
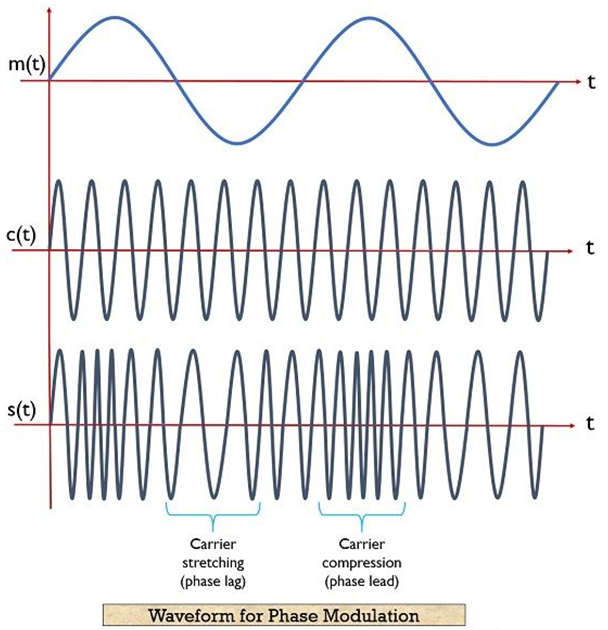
- Phase Modulation can be defined as the Phase of the carrier (Ø) signal being varied proportionally to the Amplitude of the input modulating signal.
- It is the angle modulation in which the phase of the carrier wave is changed according to the amplitude of the modulating signal.
- In phase modulation of an analog signal, the phase change is a continuous back-and-forth movement.
- The phase modulation of the digital signal is generally known as phase shift keying.
Applications of Phase Modulation
- Phase modulation is used in the transmission of radio waves. This process is also employed in wireless signal transmission like satellite and Wi-Fi transmission etc.
