- This metal can-packaged bipolar PNP transistor has a high current of 600 mA and a low voltage of 40 v. When the base is linked to the ground or has no supply, it is said to be forward biased; however, as soon as the base pin receives a signal, it becomes reverse biased. The transistor’s DC gain ranges from 100 to 300, demonstrating the amplification power of the device. Because it is employed in switching and amplification.
- The saturation area of the transistor occurs when it is fully biased, allowing a maximum of 500mA of current via the collector and providing a maximum voltage (collector to emitter) of 1.6v. The transistor is in its off state and the cut-off region while the base current is being eliminated.
- The 2n2907 transistor is a PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) designed for low-power amplifying and switching applications. It has a high current of 600mA and a low voltage of 40V. It has three terminals: an emitter, a base, and a collector. Because it is utilized for switching and amplification applications, it has a DC gain of 100–300, which shows its amplification capacity.
- The conduction current in the circuit is carried out by the electrons and holes in this bipolar PNP transistor. But in this transistor, holes make up the majority of the charge carriers.
- It is made of semiconductor-related components. The N-type layer is present between the two P-type materials since this is a PNP transistor. The base terminal is represented by the N-side, which has a negative polarity. The emitter terminal is represented by the P-side, which has positive polarity.
- Because the lowest current at the base terminal regulates the maximum current at the emitter and collector terminals, it is also known as a current-controlled device.
- The base terminal of the transistor is polarised negatively concerning the emitter terminal while it is in the conducting condition. Reverse bias occurs at the junction of the collector and base. so that the collector terminal’s polarity is opposite that of the base terminal.
- Since NPN and PNP transistors function identically, the only difference between them is that the PNP transistor’s voltage and current polarities are the opposite of those of the NPN transistor.
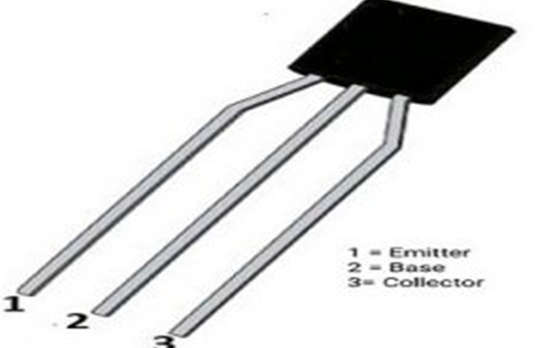
2N2907 Pin Configuration
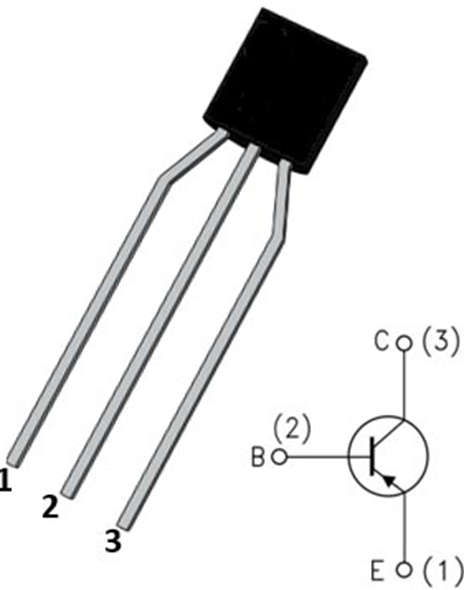
- A 3-pin or 3-terminal transistor is a 2n2907 device. It has terminals, leads, or pins for the Emitter, Base, and Collector. Below is an explanation of the 2n2907’s pin arrangement and description. Below is a diagram of the basic 2n2907 PNP transistor’s pin arrangement.
- Pin 1 (Emitter): The current of the transistor drains out through this pin.
- Pin 2 (Base): The biasing of the transistor is controlled through the base terminal.
- Pin 3 (Collector): Through this terminal, the current flows into the transistor.
- The base currency should be capable of controlling high currents at the collector and emitter terminals to facilitate amplification.
- The emitter terminal is strongly doped, while the collector terminal is very slightly doped.
- The size and doping levels of the emitter and collector terminals are different from one another.
Applications of 2N2907 Transistor
- A few 2N2907 transistor applications are given below.
- This type of transistor is used in lower power amplification circuits.
- It is used in several applications of switching circuits.
- It is used in manufacturing dual LEDs, sirens, or lamp flashers.
- It is used in analog and linear amplification.
