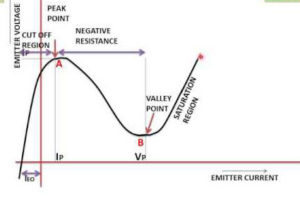
- The V I Characteristics of UJT (unijunction transistor) is show in above fig.
- The emitter voltageVE is applied between emitter E and base B1. VE is positive with respect B1. Let increasing this voltage from zero.
- The PN junction is reverse biased and emitter current IE is negative as long as the emitter voltage VE< η VBB as shown by the curve PS.
- The current flowing are very close to the reverse leakage current of PN junction reverse biased.
- At point B, the emitter voltage VEis equal to ηVBB +VD the PN junction is forward biased and UJT starts conducting.
- The point B is known as the peak pointand the voltage and current across its known as peak point voltage (VP) and peak point current (IP) respectively.
- The emitter voltage VE decreases with increase in emitter current IE. Due to drop in resistance rb1 with increase in the value of IE reduction in voltage across UJT.
- Thus the device exhibits a negative resistance region as shown by the curve BC.
- The entire base region is saturated at point C and rb1 does not decrease any more. As shown in curve CQ, the rise in voltage VEso further increase in IE.
- The point C is known as valley voltageand the voltage and current across is known as valley voltage (VV) and valley current (IV).