- Soil moisture sensors measure the water content in the soil and can be used to estimate the amount of stored water in the soil horizon. Soil moisture sensors do not measure water in the soil directly. Instead, they measure changes in some other soil property that is related to water content in a predictable way.
- For a soil sensor to work, no matter the type, it must make contact with the soil. The highest accuracy will be obtained when the soil sensor is surrounded by the soil, with no gaps between the probe and the soil.
![]()
There are two types of soil moisture sensor
-
- One that measures moisture through the electrical properties of the soil: dielectric constant, resistance & ions, and
- the other measures water potential through the use of gypsum blocks and tensiometers.
Soil Moisture Sensor : Principle of Operation
- A Soil Moisture Sensor can either use resistance or capacitance changes to measure the water content of the soil. To further understand both working principles, we’ll take a look at how each of them works.
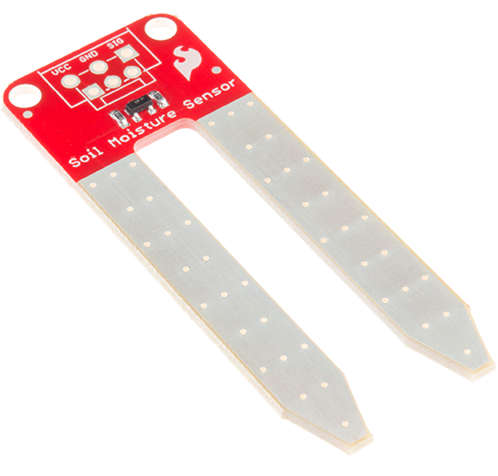
Resistive Soil Moisture Sensor:
- A resistive soil moisture sensor works by using the relationship between electrical resistance and water content to gauge the moisture levels of the soil. You’ll observe these sensors to possess two exposed probes that are inserted directly into the soil sample.
- An electrical current is sent from one probe to the other, which allows the sensor to measure the resistance of the soil between them.
- When the water content in the soil is high, it has higher electrical conductivity (water is a good conductor of electricity!). Hence, a lower resistance reading is obtained which indicates high soil moisture.
- When the water content in the soil is low, it has poorer electrical conductivity. Hence, a higher resistance reading is obtained, which indicates low soil moisture.
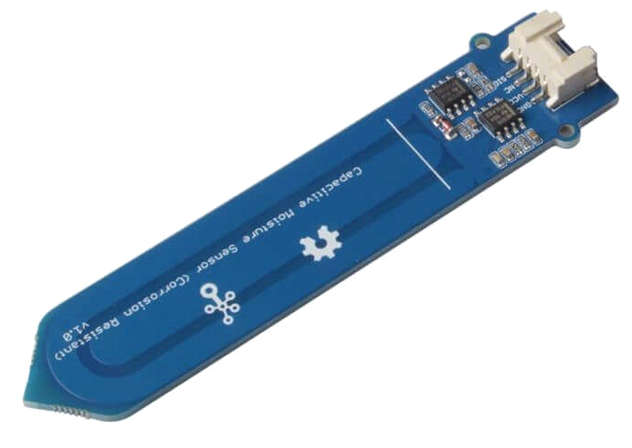
Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor:
- A capacitive soil moisture sensor works by measuring the change in capacitance. In simple terms, capacitance measures the amount of electrical charge that can be stored across an electrical potential. A capacitive soil moisture sensor is commonly built with a positive and negative plate, which are separated by a dielectric medium in the middle.
- In this case, the soil is the dielectric medium, and its capacitance changes with moisture content. By pairing the sensor with a timer circuit, we obtain an analog voltage that can be read with an Arduino board. This voltage in turn has a direct relationship with the soil moisture content.

Applications of Soil Moisture Sensor
- Agriculture
- Landscape irrigation
- Research
- Simple sensors for gardeners
- Archeology
- Biofuel studies
- Drought Forecasting Model
- Monitoring soil moisture will not only benefit environmental researchers but farmers, golf course superintendents, archeologists, and regulators. Soil moisture sensors play an important role in helping to protect water resources and understand our ever-changing climate.
