- A rheostat is an electrical device that uses smoothly variable resistance to alter the direction of current in an electric circuit. Greek phrase that means the current controlling mechanism was given by Sir Charles Wheatstone, a British physicist.
- By manually adjusting the resistance, the rheostat is a variable resistor used to regulate the flow of electricity. It is a sizeable resistor type that is utilized in situations that call for resistance or current modification. In a circuit, a rheostat is connected in series. Rheostats have higher control over current than other forms of variable resistors.
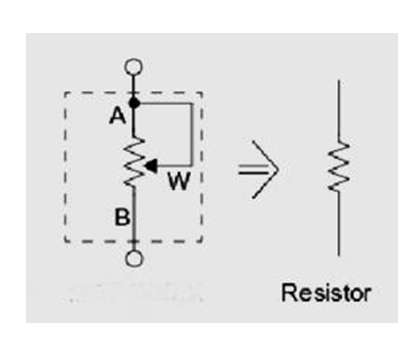
Symbol
- The most often used rheostat symbols are depicted above, however other standards use different symbols.
Working Principle
- R = V / I, where R is resistance, is the foundation of a rheostat.
- The voltage is V.
- I = present
- The inverse relationship between resistance and current is evident from the aforementioned law. This implies that the current reduces when the resistance rises and vice versa.
- In addition, using the following equation: R = L/A
- where resistance, or R
- is resistance.
- L = length A = cross-sectional area
- Resistance is inversely correlated with length. As a result, resistance rises as wire length (i.e., turn count) grows.
Working
- Let’s use the example of a rheostat that is connected in series with a DC motor field to better understand how this works. When it comes to how well a DC motor performs, the field current must be carefully controlled, and it works best when it is connected in series with the field.
![]()
- According to the connection illustration above. Even though just a fixed point and variable point are often needed, all three points/terminals may be used in some circumstances.
![]()
- The wiper point and one of the fixed points are connected in the above figure to eliminate the possibility of the motor armature/field becoming open-circuited if the variable/wiper point loses contact with resistance or rheostat (being a moving point). Similarly, when it is used as a potential divider, all three points are used.
Types of Rheostats
Rheostat types are divided into three. Rotary, linear and preset rheostats.
Rotary Rheostats:
- The rotary rheostat’s resistive element can be circular or angled. The wiper in this type of rheostat rotates. These are typically found in power applications. Rotary rheostats are more commonly used than linear rheostats due to their small size.

Linear Rheostats:
- Because the resistive element is shaped like a cylinder, they are also known as cylindrical rheostats. The wiper moves linearly in this type of rheostat. In research and development laboratories, linear rheostats are frequently used.
Preset Rheostats:
- These are small and consist of nothing more than a rheostat. Trimmers or preset rheostats are used to calibrate a printed circuit board.

Applications of Rheostat
- Changing the intensity of a light bulb’s light. A decrease in rheostat resistance reduces the flow of electric current, causing lights to dim, and vice versa.
- Generators
- Motor speed
- Heater and oven temperature control
- Volume control
