Construction:
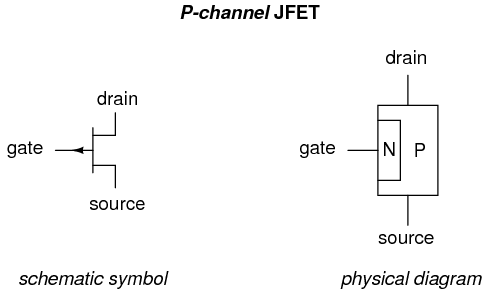
- The construction of P channel JFET is similar to the N channel JFET excepts that it consist of a P type silicon bar with two N type heavily doped regions diffused on opposites sides of its middle part.
- The JFET in which the current conduction takes place only due to holes as majority charge carriers is known as P channel JFET.
- The two PN junctions are form by the N region and the space between i.e. P regions is called a channel. A single wire is taken in the form of the terminal when both the N type regions are connected internally known as the gate (G).
- The electrical connection which is also known as ohmic contact are made to both ends of the P type semiconductor and are taken out in the form of two terminals called drain (D) and source (S).
- The drain (D) is a terminal through which electrons enter the semiconductor bar and from through which the electrons leave the semiconductor is source (S) terminal.
