- Memory cards act as electronic storage for your devices by storing digital media such as photos and videos. If you have a camera, camcorder, drone, or mobile device, chances are you use a memory card.
![]()
- The SD and microSD variants are most commonly used in smartphones and digital cameras.
- They fit into everything from your DSLR to your Nintendo Switch. However, not all cards are created equal – different devices require a different type of memory card.
What is a Micro SD Card?
- The SD in a Micro SD card stands for ” Secure Digital ” and is a non-volatile memory card that means a type of computer memory that keeps the stored data even after a power supply is detached. The format was developed by the SDA organization to utilize portable devices.
- Introduced in 2005 and widely used in smartphones, tablets, and other handheld devices, microSD is electrically and software compatible with the full-size SD card. This type of memory card is electrically & compatible with software through the full-size secure digital card.
- Subsequent versions, including SDHC (High Capacity) and SDXC (Extended Capacity), greatly increased storage. Weighing less than one gram, 1TB SDXC cards became available in 2019. The SD cards/Micro SD cards are extensively used in different applications like data logging, visualization, etc. These SD cards can be accessed easily through an adapter module of a micro SD card. This module is very simple to use with an SPI interface & a 3.3V voltage regulator is used to give proper supply to the SD card.
Pin Configuration of Micro SD Card
![]()
![]()
| Pin No. | Pin Name | In SD mode | In SPI Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pin 1 | DAT2/X | Connector Data line 2 | No Use |
| Pin 2 | DAT3/CS | Connector Data line 3 | Chip Select |
| Pin 3 | CMD / DI | Command/Response Line | Data input |
| Pin 4 | VDD/VDD | Power supply (+3.3V) | Power supply (+3.3V) |
| Pin 5 | CLK/SCLK | Clock | Serial Clock |
| Pin 6 | VSS/VSS | Ground | Ground |
| Pin 7 | DAT0/D0 | Connector Data line 0 | Data Out |
| Pin 8 | DAT1/X | Connector Data line 1 | No Use |
Features & Specifications of Micro SD Card
- Operating Voltage: 2.7V to 3.3V.
- Capacity: 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, 32GB etc.
- File System: SD/SDHC/SDXC.
- Storage System: FAT12 and FAT16.
- Transfer Speed: 95 Megabytes per second (typically).
- Speed Class: Class 2 to Class 10.
- Form Factor: 11mm × 15mm × 1mm.
Types of Micro SD Cards
MicroSD cards share the same four SD standards as SD cards. The four SD standards for microSD cards are.
| Type | Capacity |
|---|---|
| microSD | 2GB and under |
| microSDHC | More than 2GB, up to 32GB |
| microSDXC | More than 32GB up to 2TB |
| MicroSDHC | More than 2TB up to 128TB |
How to use an SD Card
- The SD cards can work in two operating modes, one is using the SD mode commands and the other is SPI mode. Most Digital cameras and mobile phones will use the SD mode to communicate with the SD card, however, this is not of our interest because only the SPI mode to communicate between an SD card and a Microcontroller like Arduino (Atmel), PIC, AVR, etc. A simple connection diagram for SPI with a microcontroller is shown below.
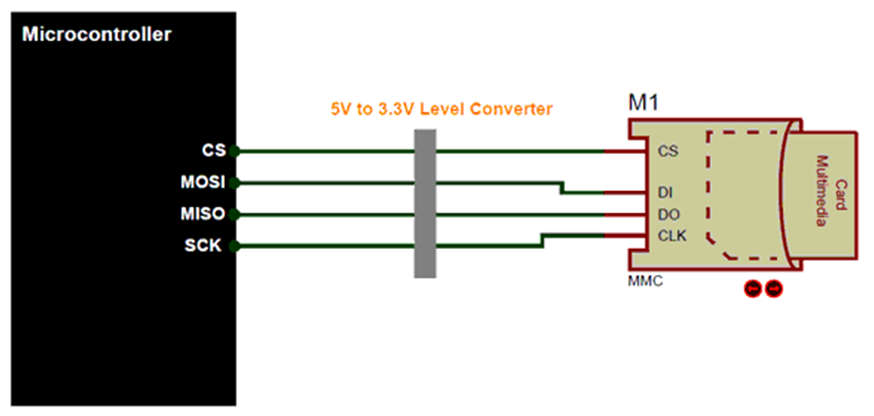
- The SPI communication requires only four wires and is vastly supported by most of the microcontrollers. However, the SD card operates with a voltage of 3.3V and all its pins speak with only 3.3V, Microcontroller, on the other hand, might work with +5V in those cases a bi-directional logic level shifter (like 74HC245) that can convert the 5V signals to 3.3V is recommended. Once you have interfaced the Card you would have to initialize it and then start communicating with it through the SPI commands.
Applications of Micro SD Card
- Portable Electronics.
- Data Loggers
- Graphical Displays.
- MP3 players.
- Audio file handlers.
- Image handlers.
