A German Physicist Gustav Robert Kirchhoff introduces the law in 1845.
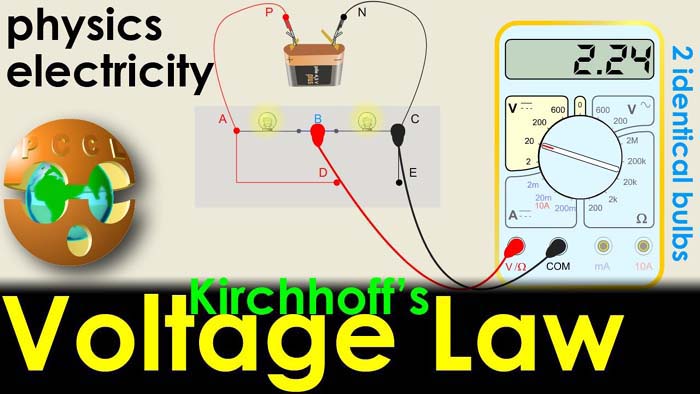
KVL is one of the fundamental laws used for circuit analysis. KVL is Kirchhoff’s second law that deals with the conservation of energy around a closed circuit path and is also known as Kirchhoff’s loop.
KVL states that in any closed loop network the total voltage around the loop is equal to the sum of all the voltage drops within the same loop, which is also equal to zero. In other words, the algebraic sum of all voltages within the loop must be equal to zero.
Applied voltage=Sum of all voltage drop
Application
- One can easily find different parameters of a circuit line resistance current or voltage quite easily. It explains that the sum of voltage in an enclosed circuit is always equal to zero. It is applied for voltage measurements in a circuit.