- Electromagnetic field is the physical field produced by charged particles as we see the term electromagnetic it has two part electric and magnetic field. The term can be spitted into two field electric field and magnetic field.
- Electric field is produced because of statics charges whereas the magnetic field is produced because of the charges moving what we exactly called as current. It is necessary to study both the field together with an electromagnetic field. Hence electromagnetic field theory can be defined as the study of electric and magnetic field subject to the state of the source.
- Do you know if you hear the word electric field the scenario before us is that there it is certain charge weather charge may be positive or negative and the region increased because of that particular charge we called that region as electric field.
![]()
- In this diagram we see the two charges denoted by positive Q and negative Q. The lines what we term as electric flux line are always going away from the positive charge where as in the case of negative charge these lines are always coming towards it so a node not can be done that the electric flux lines are always generated on positive charge whereas they anymore negative charge. So this is a general representation or general understanding of electric field.
![]()
- Now regarding magnetic field always the picture comes into the mind that is bar magnet. In diagram the magnet and having two poles, North and South pole shown the bar magnet is also surrounded by some lines what we call magnetic flux line here also the magnetic flux line always originate at the north pole and South pole.
- Now in case of charged particle, the charge is steady condition which produces electric field whereas when it is in dynamic condition when it is in motion we say it is flow of current so if we have a conductor flowing current in particular direction so that cannot conductor will be surrounded by the magnetic flux lin.
![]()
- In this diagram the conductor is shown the current in the upward direction is surrounded by the magnetic flux line, the orientation of magnetic flux line is always determined according to the right hand thumb rules come in the direction of current and current fingers gives you the direction of magnetic flux. Now these two examples has given us the scenario of electric field and magnetic field separately. Now the electromagnetic field together the common example we have is electromagnetic wave the light what we get from any source is basically electromagnetic wave.
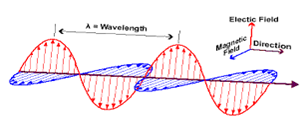 So let see electromagnetic wave, this is diagram where the representation of electromagnetic wave simply you move is shown in three dimensional space here the co-ordinate axis r3 and data manually perpendicular to each other electric field varies in this diagram in vertical plane whereas magnetic field varies in the horizontal plane. The third direction shown by this axis gives you the direction of propagation of wave.
So let see electromagnetic wave, this is diagram where the representation of electromagnetic wave simply you move is shown in three dimensional space here the co-ordinate axis r3 and data manually perpendicular to each other electric field varies in this diagram in vertical plane whereas magnetic field varies in the horizontal plane. The third direction shown by this axis gives you the direction of propagation of wave.- Let us focus on the second point what are the inspiration behind the research and development in the field of electromagnetic field theory. Electromagnetic field is the fundamental force in the nature like gravitational force whatever the naturally happening process we see which transform energy from one form to another form these actually is the biggest inspiration behind the research and development rather the curiosity develop by scientist in the domain.
