- Fairchild Semiconductors have a list of high voltage IGBTs under the FGAxxN120 series. All the IGBT under this series features Non-Punch Though (NPT) Technology hence it has very low switching loss and low saturation voltage making it feasible to be used in low voltage switching driver designs with comparatively high efficiency for its switching range.
- The current rating of this IGBT is denoted after the prefix FGA. For example, the FGA15N120 IGBT is rated for 15A Collector current at 125°C similarly the FGA25N120 is rated for 25A. The number 120 indicates that the IGBT has a collector-emitter voltage of 1200V.
Pin Configuration
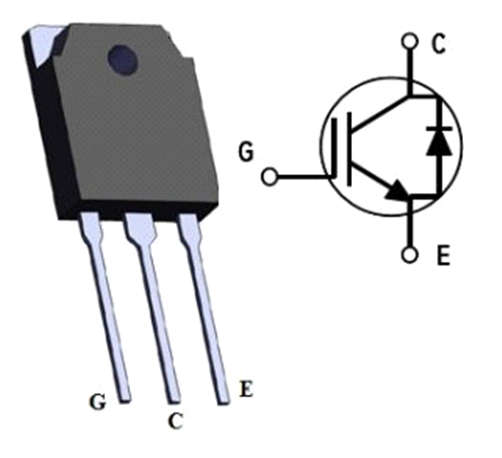
- Pin1 (Gate): This gate terminal is used to control the biasing of the IGBT.
- Pin2 (Collector): This collector terminal is used to allow the flow of current.
- Pin3 (Emitter): Current flows out from this terminal.
Features of FGA15N120 IGBT
- High Voltage IGBT with low saturation voltage.
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): 1200V.
- Collector Current (IC): 30A @25°C.
- Minimum Gate threshold voltage (VGE) is 4.5V.
- Maximum Gate threshold voltage (VGE) is 8.5V.
- Gate-Emitter Voltage (VGE) is ±20V (max).
- Rise time and fall time are about 20ns and 100ns respectively.
- Available in To-3P package.
Where to use FGA15N120 IGBT
- The FGA15N120 is a high voltage IGBT, it can be used to switch high voltage values as high as 1200V with a current capability of 30A at 25°C. It can further handle high pulse currents of up to 45A making it suitable in an application where high voltage and switching current spikes are involved.
- The 15N120 IGBTs have extended avalanche capability that is the IGBTs are immune to stray inductance problems. Even when the Collector-Emitter voltage exceeds the rated voltage they do not have a breakdown because of this property. Hence these IGBT can be used in rugged switching designs.
- Like all IGBT the FGA15N also suffers from low switching speed and a high voltage drop across collector and emitter compared with MOSFETs. So if your design requires high efficiency and a faster switching device then you should prefer MOSFETs over IGBT. IGBT is preferred in designs where high switching voltage and current are involved.
How to use FGA15N120
- An IGBT is a combination of MOSFET and BJT, as we can notice from its pin-out. It has Gate on the input side similar to a MOSFET and Collector and Emitter on the output side similar to a BJT. This indicates that an IGBT is simply a MOSFET coupled with BJT on its output side to utilize the merits of a MOSFET and BJT.
- Similar to MOSFET in IGBT also the gate pin has to be triggered with the minimum gate voltage to close the switch. Here in FGA15N120 the minimum gate saturation voltage is 4.5V but normally 5V is used in designs, the required gate trigger voltage can be calculated using the collector-emitter voltage and collector current that has to be switched, using the graph in the datasheet as shown below.
- Once the gate is triggered the IGBT will remain on even after the trigger voltage is removed similar to a MOSFET. This is because of the gate capacitance present on the input gate pin of the IGBT. To turn off the device the gate capacitance has to be discharged by simply connecting the gate pin of the IGBT to the ground. Because of this normally the Gate pin of the IGBT is connected to the ground through a pull-down resistor of 10k or a gate driver IC like IR2104 is used.
- When IGBT is used in switching circuits, care should be taken that it is not used in high-frequency designs since the collector-emitter voltage drop (switching loss) of the IGBT increase with the increase in switching frequency. The graph for the same can be found in the datasheet.
Applications of FGA15N120 IGBT
- High Voltage, high current switching device
- Induction Heating
- Microwave Oven
- Large Solenoids
- Tesla Coils
- Converters or Inverter circuits