- In data communications and networking, (OFDM) is a method of digital data modulation, whereby a single stream of data is divided into several separate sub-streams for transmission via multiple channels.
- OFDM uses the principle of frequency division multiplexing, where the available bandwidth is divided into a set of sub-streams having separate frequency bands.
- In 1966 OFDM is introduced by Chang at Bell Labs and was improved by Weinstein and Ebert in 1971.
Working Principle of Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- In OFDM, each bit may be represented by a 1 nanosecond segment of the signal, with 0.25 ns spacing between bits.
- It is used to split the signal across four component streams letting every bit be represented by 4 ns of the signal with 1 ns spacing between.
- The signal integrity is higher and the overall data rate is the same, 4 bits every 5 ns.
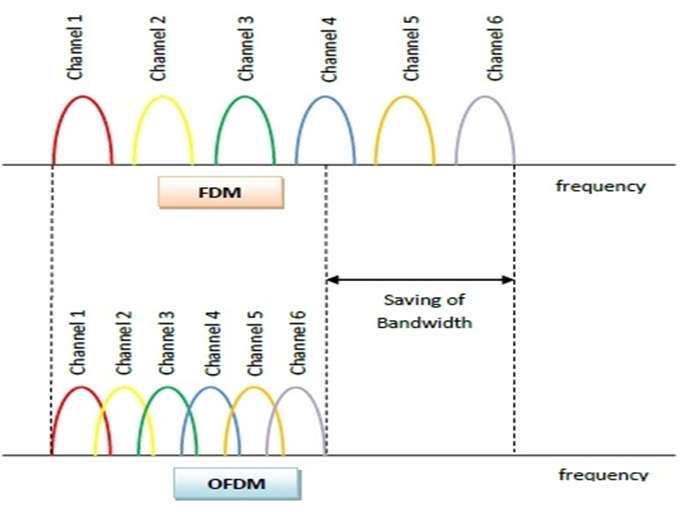
- It builds on simpler frequency-division multiplexing (FDM).
- The total data stream is divided into several subchannels in FDM, but the frequencies of the subchannels are opposite to space so they do not overlap or interfere.
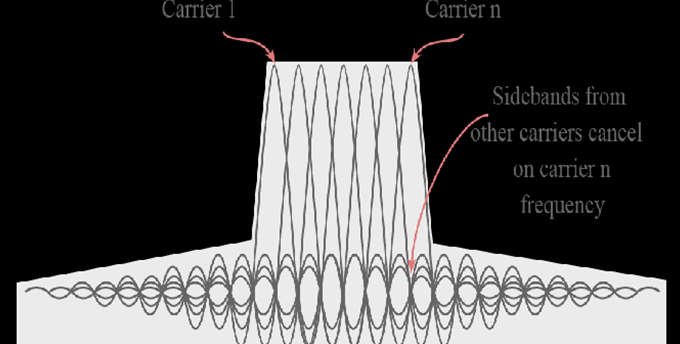
- The subchannel frequencies are adjacent and overlapping but are still orthogonal, in that case, they are carefully chosen and modulated so that the interference between the subchannels is not done.
Advantages of Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- Immunity to Selective Fading: The main advantage of OFDM is that is more resistant to frequency selective fading than single carrier systems because it divides the overall channel into multiple narrowband signals that are affected individually as flat fading sub-channels.
- Resilience to interference: Interference appearing on a channel may be bandwidth limited and in this way will not affect all the sub-channels. This means that not all the data is lost.
- Spectrum Efficiency: Using close-spaced overlapping sub-carriers, a significant OFDM advantage is that it makes efficient use of the available spectrum.
- Resilient to ISI: In this advantage of OFDM is that it is very resilient to inter-symbol and inter-frame interference. This results from the low data rate on each of the sub-channels.
- Resilient to Narrow-Band Effects: Using adequate channel coding and interleaving it is possible to recover symbols lost due to the frequency selectivity of the channel and narrowband interference. Not all the data is lost.
- Simpler channel equalization: One of the issues with CDMA systems was the complexity of the channel equalization which had to be applied across the whole channel. An advantage of OFDM is that by using multiple sub-channels, the channel equalization becomes much simpler.
Disadvantages of Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- High Peak to Average Power Ratio: An OFDM signal has a noise-like amplitude variation and has a relatively high large dynamic range, or peak to average power ratio. This impacts the RF amplifier efficiency as the amplifiers need to be linear and accommodate the large amplitude variations and these factors mean the amplifier cannot operate with a high-efficiency level. Sensitive to carrier offset and drift: In this disadvantage of OFDM is that is sensitive to carrier frequency offset and drift. Single carrier systems are less sensitive.
Applications of Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- It is used in Wi-Fi, DSL internet access, 4G wireless communications, digital television, and radio broadcast services.
