- Universal Serial Bus (USB) was developed in the 1990s to simplify the connections between computers and peripheral devices. It has become widely popular due to its compatibility with many platforms and operating systems, its low cost of implementation, and its ease of use. Most computers that are built today come with several USB ports, and USB is the interface of choice for most home and office peripherals including printers, cameras, modems, and portable storage devices.
- Micro USB connectors exist in four connector types: micro USB type A, micro USB type B, Micro USB 2.0, and micro USB 3.0. Micro USB 3.0 is much like micro type B but with an additional pin group on the side for twice the wires, enabling USB 3.0’s greater speed. Similar to typical USB, the micro types are plug & play.
- USB has some standards which the industry body has to maintain which are known as the USB-IF ( USB Implementers Forum). In its actual specification, USB identified simply two types of connectors like A & B.
Pin Configuration
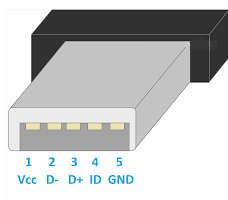
- Pin 1 ( VCC ) It is +5VDC and the connected wire color is red.
- PIN 2 ( D- ) White Data + and the connected wire color is green.
- Pin 3 ( D+ ) Green Data + and the connected wire color is green.
- Pin 4 ( ID ) More detects and the connected wire color is blue.
- Pin 5 ( GND ) Ground and the connected wire color is black.
Specifications
- Micro USB is a Type B or SMT.
- These are available as a drop-in, reverse mount & standard.
- Gender is Female.
- Contact resistance is 30mΩ at 100mA.
- The number of Pins is 5.
- Max voltage rating is 30V.
- The mating cycle is above 5k times.
- The current rating is 1A.
Types of Micro USB
1. Micro-A USB
- Micro-A USB is used by small current devices like cell phones, GPS units, digital cameras, etc. The transfer rate is 480 Mbps, it is high-speed as compared to Mini-USB. This cable includes a female connector only and it is available in a rectangular shape.

2. Micro-B USB
- This connector can be found on mobile devices such as cellphones, GPS units, and digital cameras. Micro-USB B offers a connection physically smaller in size than a USB Mini-B, while still supporting the high-speed transfer rate of 480 Mbps. The connection can be easily identified by its black-colored receptacle and compact 5-pin design.

3. Micro-B USB 3.0
- The USB 3.0 Micro-B connector is found on USB 3.0 devices. This connector is designed to carry data and power in USB Super Speed applications. Cables with this connector are not backward compatible with USB 2.0 or USB 1.1 devices.

Applications of Micro-USB
- Micro USB cables are largely used with Android devices to charge your phone or tablet and transfer data to your computer, but many digital cameras, tablets, smartwatches, toys, battery charging packs, photo printers, GPS systems, and older smart products use these cords too. However, manufacturers rarely produce technology that uses micro USB cords today, as many companies are switching to USB-C connectors. While micro USB was the reigning standard, which meant you could keep your cords when upgrading devices, buying a new phone or tablet now may also require a new set of charging cables.
- Another reason why developers are moving away from the micro USB is that it is limited in its ability to transmit video or audio information. While these cables can be connected between devices, they require an adapter, such as a USB-to-HDMI converter, to translate the signals properly into something the output device can interpret and present. Converter connectors potentially add a wider variety of uses to the micro USB’s capabilities, even if these functions aren’t possible with the cable alone. The USB-C invention eliminates these drawbacks, making it easier for consumers to procure just one cord for many uses across products.
