- Tantalum capacitors are a subtype of electrolytic capacitors, a passive component of the electronic component. It is made up of an anode made of porous tantalum metal, an insulating oxide layer that serves as the dielectric, and a cathode made of liquid or solid electrolyte. Tantalum capacitors are distinguished from other conventional and electrolytic capacitors by their high capacitance per volume (high volumetric efficiency) and lower weight due to their very thin and relatively high permittivity dielectric layer.

- Electrolytic capacitors, like standard capacitors, store electrical energy. It stores electrical power in a dielectric oxide layer between two conductors by separating charge in an electric field.
- The cathode is the solid electrolyte, which serves as another electrode in the capacitor. An electrolytic capacitor differs from a supercapacitor or an electrochemical capacitor in that the electrolyte is typically the ionic conductive connection.
- A positive voltage is applied to the tantalum electrolyte capacitor’s anode. A thin oxide layer is formed as a result of the applied voltage. This oxide layer serves as the capacitors’ dielectric material.
Construction of Tantalum Capacitor
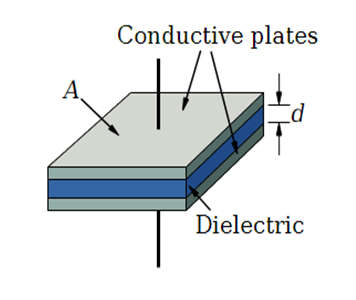
- A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is a blemish capacitor made of tantalum powder sintered into a capsule that serves as the capacitor’s anode. Tantalum pentoxide is used to make the oxide layer, which acts as a dielectric. The capacitor’s cathode is a stable manganese dioxide electrolytic.
Differences
Difference Between Tantalum and Typical Electrolytic Capacitor
- Aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors are the three types of electrolytic capacitors.
- The main distinction between tantalum and electrolytic capacitors is that tantalum capacitors use a sintered pellet of high purity tantalum powder as the dielectric component, whereas electrolytic capacitors have an anode or a positive plate made of a metal that can form an oxide layer through anodizing.
- The anode’s tantalum material allows it to oxidize easily, just like an aluminum capacitor, and also allows it to benefit from the increased conductivity when tantalum powder is pressed against a conductive wire. The oxide then forms on the surface and within the material’s cavities. This results in a larger surface area and a greater ability to store charge with higher permittivity than aluminum.
- Niobium-based capacitors use a mass of material wrapped around a wire conductor to create a dielectric via oxidation. These dielectrics have higher permittivity than tantalum capacitors but require more dielectric thickness for the same voltage rating. Because tantalum capacitors have become more expensive, these capacitors have been used more frequently recently.
Difference between Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitor
- Aging is defined as a logarithmic decrease in capacitance over time in capacitors. Tantalum capacitors age, whereas ceramic capacitors do not. Tantalum capacitors do not even have a known wear-out mechanism.
- Tantalum capacitors are almost always polarized. This means they can only be connected to a DC power supply while maintaining the correct terminal polarity. Ceramic capacitors, on the other hand, are non-polarized and can be connected to an alternating current source safely. Ceramic capacitors have a better frequency response because they are not polarized.
- Tantalum capacitors typically exhibit linear capacitance changes when subjected to temperature changes, whereas ceramic capacitors typically exhibit non-linear responses. Ceramic capacitors, on the other hand, can be made to trend linearly by restricting the operating temperature ranges and accounting for temperature response during the design phase.
- Tantalum capacitors exhibit consistent stability when capacitance changes with applied voltage, whereas ceramic capacitors do not. The permittivity of the dielectric shrinks within the ceramic capacitor in response to higher applied voltages, causing capacitance changes. Though most ceramic capacitor capacitance changes are linear and easily accounted for, some higher permittivity dielectrics can lose up to 70% of their initial capacitance when operated at rated voltage.
Applications of Tantalum Capacitor
- Because of their low leakage current, high capacity, and long-term stability and reliability, they are used in sample and hold circuits that rely on low leakage current to achieve long hold duration.
- Tantalum capacitors are also available in military specifications (MIL-SPEC) versions that have tighter tolerances and a wider operating temperature range.
- • Because of their small size and long-term stability, they are also commonly used for power supply filtering on computer motherboards and cell phones, most often in surface mount form.
- • Tantalum is also used in medical electronics due to its high stability. Tantalum capacitors are sometimes used in audio amplifiers where stability is critical.
