What is Weight Sensor?
- A weight sensor is a particular kind of transducer, more especially a weight transducer, by definition. It transforms a mechanical force that is applied as an input, such as load, weight, tension, compression, or pressure, into another physical variable, in this case, an electrical output signal that can be measured, converted, and standardized. The electrical signal varies proportionally to the force being applied to the sensor.
- There are numerous choices for measuring a stable weight, yet a single load cell can handle loads of any magnitude. Weight sensors, often known as load cells, are divided into various categories. Weight sensors are used primarily to measure weight in various applications. The four most common weight sensors are hydraulic, pneumatic, capacitance, and strain gauge.
- The first two of the aforementioned sensor kinds are electrical transducer devices. It is a sensor that produces voltage as output after detecting a physical stimulus.
- The other two sensors do not overtly produce output like electrical signals, however, they can still have their output depending on the application situation. The strain gauge is the sensor that is most frequently used in a variety of fields, including home, automation, healthcare, and automotive.
Working of Weight Sensor
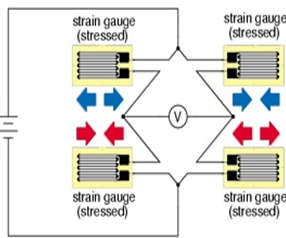
- First, we must comprehend the physics and material science that underlie the strain gauge, the fundamental component of the strain weight measurement system (sometimes referred to as Strain gauge). A sensor called a metal foil strain gauge changes electrical resistance in response to the applied force. To put it another way, it transduces—or converts—force, pressure, tension, compression, torque, weight, etc. into a change in electrical resistance that can be measured.
![]()
- The metal body works as a “spring,” deforming slightly when force (tension or compression) is applied. Unless it is overloaded, it then returns to its previous shape. A Wheatstone Bridge circuit generates a differential voltage variation as a result of the strain gauge’s changing shape and electrical resistance as a result of the flexure’s deformation. As a result, the voltage output from the load cell circuit may be used to compute the physical force exerted on the flexure, which is proportional to the change in voltage.
- Sensitivity and accuracy are crucial ideas in weight transducers. The smallest force that may be applied to the sensor body and still result in a linear and repeatable fluctuation in the voltage output is known as the weight sensor accuracy. The more accurate the load cell, the better because it can reliably record extremely reasonable force differences.
Applications of Weight Sensor
- They play important role in high precision factory automation, surgical robotics, aerospace, etc.
- A capacitive load cell can measure both dramatic changes and enormous weights, as well as very minute weight variances for extremely precise measurements.
- To calculate the load in cables, struts, tiebacks, foundation anchors, or rock bolts.
- Various types of anchor systems are put to the test and their performance is tracked over time.
- Measurement of the compressive load at the intersection of two structural components, such as the supports for a tunnel or the top of a pile strut.
- Correlations between data from borehole extensometers are frequently used.
