- 2N4401 is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor’s terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal.

- 2N4401 is In an NPN transistor hence the collector and emitter will be left open ( Reverse biased ) when the base pin is held at the ground and will be closed ( Forward biased ) when a signal is provided to the base pin. 2N4401 has a gain value of 500; this value determines the amplification capacity of the transistor. The maximum amount of current that could flow through the Collector pin is 800mA, hence we cannot connect loads that consume more than 500mA using this transistor. To bias a transistor we have to supply current to the base pin, this current ( IB ) should be limited to 5mA.
- When this transistor is fully biased then it can allow a maximum of 800mA to flow across the collector and emitter. This stage is called Saturation Region and the typical voltage allowed across the Collector-Emitter (V¬CE) or Base-Emitter (VBE) could be 200 and 900 mV respectively. When the base current is removed the transistor becomes fully off, this stage is called the Cut-off Region and the Base Emitter voltage could be around 660 mV.
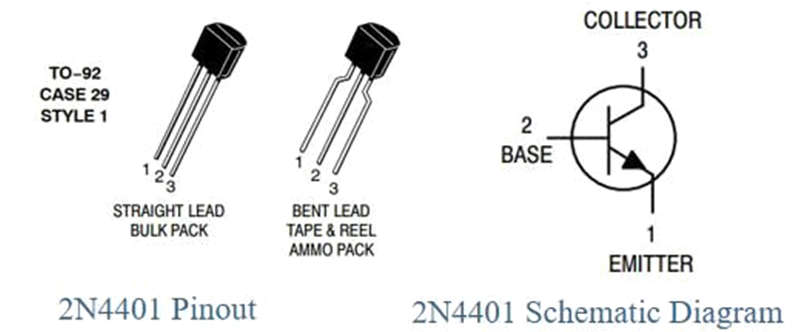
Specifications / Features
- Transistor Polarity NPN
- Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) 60VDC
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) 40VDC
- Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) 6VDC
- Continuous Collector Current (IC) 600mA
- Collector−Base Capacitance (Ccb) 6.5pF
- Transition Frequency (fT) 100MHz
- DC Current Gain (hFE) 80 ( for collector current is 10mA)
- Operating Temperature Range – 55°C to + 150°C
- Power Dissipation (PD) 1.5W
- Breakdown voltage from emitter-base (VBE) 6V
How to use 2N4401 NPN Transistor?
- The 2N4401 NPN transistor can be found in three configurations: Common-Emitter (CE ), Common-Base ( CB ), and Common-Collector (CC ). The maximum voltage is at the collector terminals as compared to the voltage at the base terminal.
- As CE configuration generates the necessary voltage as well as gain of power, it is used mostly for amplification purposes, which helps in enhancing the input signal through 20dB which is almost 100 times above the input signal.
- The combination of current at the base & collector terminals is equal to the current at the emitter terminal. Here, the differentiation of two terminals like emitter & collector can be done based on their doping concentration & size. Here, the emitter terminal is doped highly whereas the collector terminal is doped lightly.
- In this transistor, the gain of forwarding current is represented with beta (β) and is a fraction between collector current (IC) & base current (IB). here, this ‘β’ is called an amplification factor and its value ranges from 20 to 1000 however its typical value is 200.
- The gain of current for this transistor can be specified through alpha (α) and it is a fraction between collector current (IC) and emitter current (IE). Here, the value of Alpha mainly ranges from 0.95 to 0.99 but in most applications, its typical value is considered a unity.
Switch Circuit
- This transistor like all can be used either as a switch or as an amplifier. The Base-Emitter voltage of this transistor is 6V so you just have to supply this voltage across the base and emitter of the transistor to induce a base current into the transistor. This transistor will make it forward biased and thus closes the connection between collector and emitter. However, one important thing to notice is the Base resistor a.k.a current limiting resistor. As the name suggests this resistor will limit the current flowing through the transistor to prevent it from damaging. The value for this resistor can be calculated using the formula
RB = VBE / IB - The required components to build this moisture sensor circuit are; DC supply 6V, two probes, a 6V relay, 1N4007 diode, 2N4401 NPN transistor & 300k variable resistor.
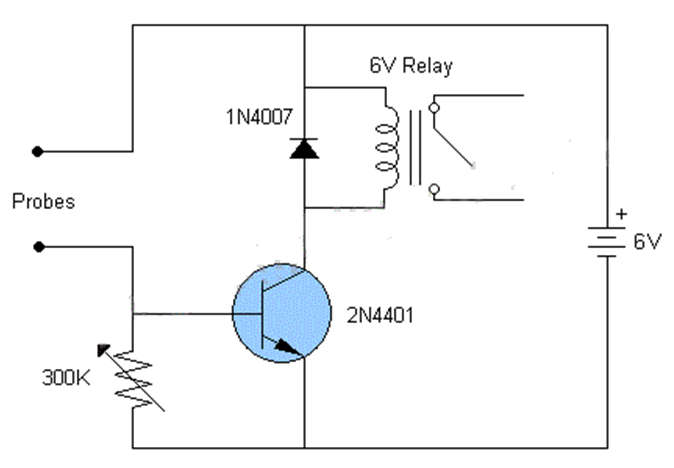
- Two probes are used to detect the moisture from the substance. A variable resistor is used to actively adjust the circuit and activate the relay on your preferred moisture range. A transistor works like a switch for the relay, so we can connect any load using the relay to control through this circuit.
- Once the two probes in this circuit detect the moisture of the substance then it allows the voltage supply throughout it to activate the transistor so that the relay will be activated. So the load which is connected to the relay will be activated immediately. This circuit operates with 6V/12V and the relay within this circuit must have a similar value to the input voltage.
Applications of 2N4401 NPN Transistor
- Audio Pre-amplifiers
- Rectifier circuits
- Sensor Circuits
- Inverter circuits
- Stages of Audio Amplifier
- It is used in different switching applications.
- It used to switch loads below 500mA
- It can be used for switching maximum current loads like up to 500mA
- Used to control the speed of a motor
- RF circuits below 250MHz
- Used as a Darlington pair transistor
